Molar mass 86.1323 g/mol
Appearance Colorless liquid
Density 0.949 g/mL
Melting point −19 °C (−2 °F; 254 K)
Boiling point 139 to 140 °C / 760 Torr
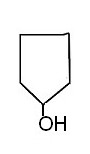
| Chemical formula C5H10O Molar mass 86.1323 g/mol Appearance Colorless liquid Density 0.949 g/mL Melting point −19 °C (−2 °F; 254 K) Boiling point 139 to 140 °C / 760 Torr |  |
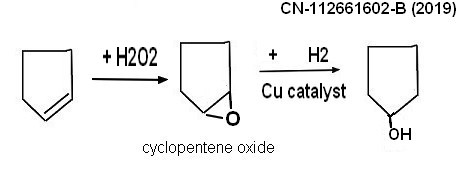
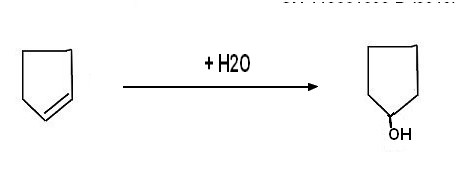
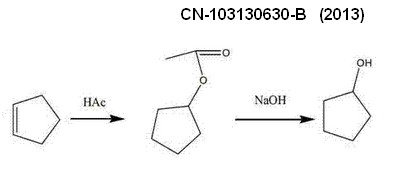 *******************************************************************
*******************************************************************